Most online shoppers don’t type exact product names. They say things like ‘shoes for standing all day’ or ‘gift for a kid who loves space’. Traditional search engines fail here. They match keywords, not meaning. That’s why 30-40% of product searches end without a click - and why 1 in 3 shoppers abandon carts after a bad search experience, according to Baymard Institute. But now, something’s changing. LLM-powered semantic matching is turning search from a typing exercise into a conversation.
Why Keyword Search Fails in E-Commerce
Picture this: a customer types ‘wireless headphones’. A basic search system looks for products with those exact words. It misses ‘Bluetooth earbuds’, ‘cordless audio’, or even ‘noise-canceling listening devices’. No synonyms. No context. No understanding.
That’s the problem. A 2024 Vectara study found keyword systems only get 45-55% of user intent right. If someone searches for ‘winter boots for snow’, they don’t want boots labeled ‘water-resistant’ - they want ‘insulated, grippy, rated for -20°C’. Keyword systems can’t connect those dots.
Result? Frustration. Abandonment. Lost sales. Retailers lost an estimated $120 billion in potential revenue in 2024 just from poor search experiences, according to MIT’s e-Commerce Lab. That’s not a small leak - it’s a flood.
How LLMs Understand What You Really Want
Large Language Models (LLMs) don’t just scan text. They learn meaning. Think of them as shoppers who’ve read every product description, review, and category label on your site - and then remembered how they all connect.
Here’s how it works: when you type a query, the LLM turns it into a vector - a string of numbers that captures meaning, not words. A product description gets turned into another vector. The system then finds the closest matches by comparing these number patterns.
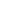
For example, the vector for ‘comfortable shoes for standing all day’ ends up near vectors for ‘arch support’, ‘cushioned sole’, ‘anti-fatigue’, and even ‘nurse shoes’. It doesn’t need you to use the right words. It just needs you to mean it.
Models like Sentence Transformers (all-MiniLM-L6-v2) do this in real time, converting text into 384-dimensional vectors. Image search works the same way: a picture of a hiking boot gets turned into a vector that aligns with text descriptions of the same boot - even if the caption says ‘outdoor trekking footwear’ instead of ‘hiking boot’. Tools like CLIP and ResNet-50 make this possible.
Real-World Results: Numbers That Matter
Companies aren’t just experimenting - they’re seeing real returns.
- Nordstrom saw a 28% drop in search-to-purchase time and a 19% boost in conversion for complex queries after switching to semantic search.
- Coveo’s clients reported a 22% increase in conversion lift compared to keyword-only systems.
- Amazon’s internal testing showed a 15-25% increase in sales when semantic matching was properly tuned.
- Users completed purchases 32% faster with semantic search, and 78% said they felt less frustrated.
These aren’t theoretical gains. They’re measurable, repeatable improvements in revenue and customer satisfaction. Netguru’s 2025 report found that 67% of top retailers now use semantic search - and those that didn’t were falling behind.

How It Works Under the Hood
Building this isn’t just slapping an AI model onto your Shopify store. It’s a system. Three parts work together:
- Vector search engine: Stores product data as numbers. Tools like ChromaDB and Milvus handle millions of vectors, with ChromaDB supporting up to 100 million per instance.
- LLM processing layer: Turns your query into a meaning-based vector. BERT and Sentence Transformers are the most common.
- Hybrid filter: Combines semantic results with traditional filters - price, brand, size - so you don’t get a $1,000 tent when you asked for something under $100.
Performance matters. If the system takes more than 100 milliseconds to respond, users bounce. That’s why Amazon developed KD-Boost, a knowledge distillation technique that trains smaller, faster models using the wisdom of larger ones. The result? 95% of the accuracy, 40% less latency.
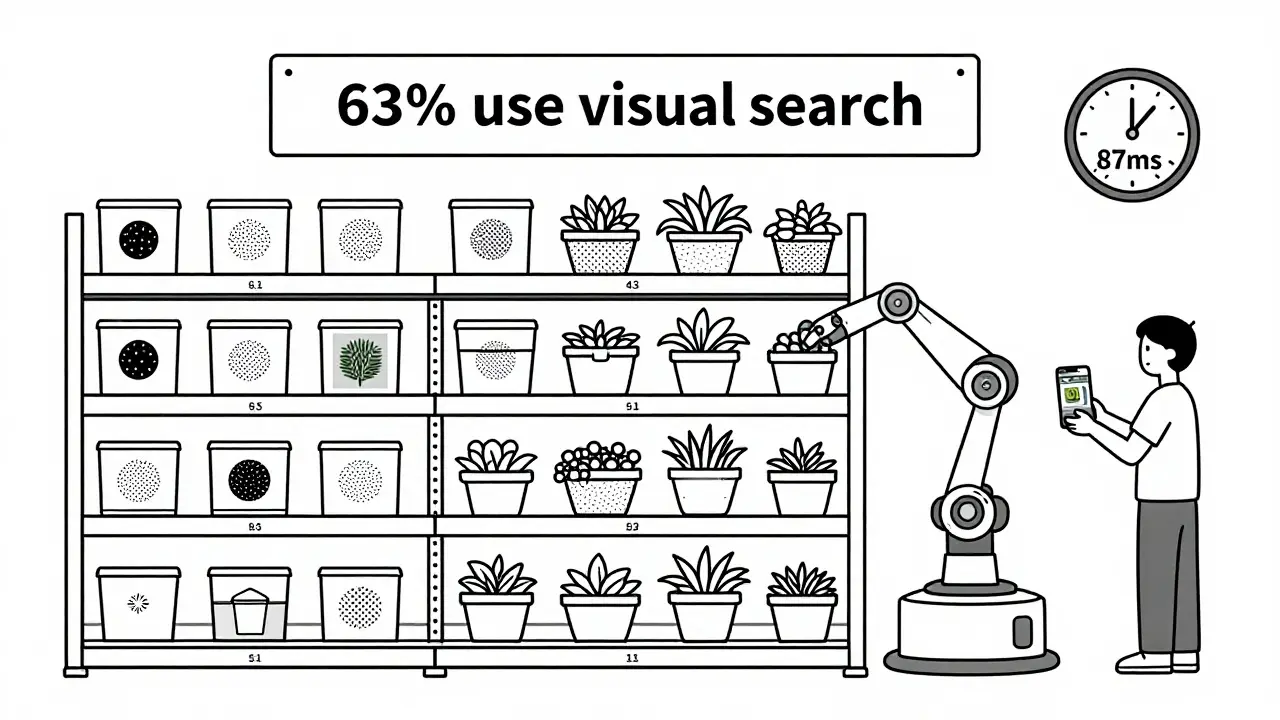
And it’s not just text. Most modern systems now handle images too. Snap a photo of a shirt you like? The system finds similar styles - even if they’re from different brands or labeled differently.
What’s Better - SaaS or Custom?
You have two paths:
- SaaS platforms like Coveo, Algolia, or Vectara: Plug-and-play. Setup takes 2-3 weeks. Good for SMBs and teams without AI engineers. Vectara scored 4.7/5 for ease of integration.
- Custom builds using open-source tools (ChromaDB, Milvus, Sentence Transformers): More control. Takes 8-12 weeks. Requires ML engineers and data specialists. Scores higher on performance - 4.5/5 on Trustpilot.
Enterprise retailers (Fortune 500) lean toward custom solutions. SMBs often start with SaaS. But here’s the catch: even SaaS tools need clean data. If your product titles are all ‘Product #12345’ and descriptions are 3 words long, no AI can fix that.
Where It Still Falls Short
LLMs aren’t magic. They struggle in two key areas:
- Technical specs: If someone searches for ‘DDR5 RAM with 6400MHz CL32’, exact keyword matching still wins. Semantic models might confuse it with ‘gaming memory’ and miss the precision.
- Filter bubbles: If you always buy running shoes, the system might stop showing you hiking boots - even if you’re planning a trip. Personalization can become limiting.
Also, multilingual support is still uneven. A query in Spanish might not map well to English product data unless the model was trained on both. And cold starts - new products with no reviews or data - still confuse the system.
What You Need to Make It Work
Want to try this? Here’s what you actually need:
- Good product data: Full descriptions, attributes (size, color, material), and clean categories. No more ‘cool gadget’ as a title.
- Historical search data: What did people search for last year? What terms led to sales? This trains the model.
- Computational power: Vector search needs memory and speed. Cloud hosting (AWS, GCP) is standard.
- One ML engineer and one taxonomy expert: You can’t outsource meaning. Someone needs to define how products relate.
Forrester gave semantic search an average rating of 4.6/5 - but warned that many retailers skip the data prep and get only 5-7% lift instead of 15-25%. It’s not the AI that fails. It’s the foundation.
The Future: Beyond Search
LLM-powered discovery isn’t stopping at search bars. It’s becoming the backbone of conversational commerce.
By 2027, Gartner predicts 60% of e-commerce interactions will start with voice or chat - not typed queries. Imagine asking, ‘What’s a good gift for my mom who likes gardening but hates weeding?’ - and getting a curated list of self-watering planters, ergonomic tools, and low-maintenance succulents.
Companies are already combining search with recommendations. 78% of semantic search systems now suggest related products based on what you’re viewing. Visual search is growing too - 63% of implementations now let you upload images.
The market is exploding. It hit $1.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit $3.8 billion by 2027. The question isn’t whether you should adopt this - it’s whether you’re ready to fix your product data before you do.
Final Thought: It’s About Trust
People don’t want more options. They want the right one - fast. LLMs make that possible. But only if your data is clean, your goals are clear, and you don’t treat this as a plug-in miracle.
The best search systems don’t just find products. They understand people. And that’s what turns browsers into buyers.
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence


Rohit Sen
January 14, 2026 AT 20:30Vimal Kumar
January 16, 2026 AT 03:47Amit Umarani
January 16, 2026 AT 08:59Noel Dhiraj
January 17, 2026 AT 20:32vidhi patel
January 18, 2026 AT 12:37Priti Yadav
January 19, 2026 AT 10:55Ajit Kumar
January 21, 2026 AT 05:55Diwakar Pandey
January 21, 2026 AT 17:37Geet Ramchandani
January 23, 2026 AT 00:16Pooja Kalra
January 23, 2026 AT 09:57