When your AI chatbot takes 4 seconds to answer a simple question, users don’t wait. They leave. And if that happens across thousands of requests daily, your cloud bill spikes while your customer satisfaction plummets. This isn’t hypothetical-it’s happening right now in production AI apps that skip caching. The truth? AI-generated web apps don’t scale without caching. Not because the models are slow, but because you’re paying to recompute the same answers over and over.
Why Caching Isn’t Optional in AI Apps
Running a large language model like GPT-3.5 or Claude 3 costs about $0.0001 per token. Sounds tiny? Multiply that by 100,000 daily users asking the same thing-"What are your business hours?" or "How do I reset my password?"-and you’re spending $100+ a day just to repeat the same answer. That’s not AI intelligence. That’s wasted compute. Companies like InnovationM cut their API costs by 70% by caching common prompts. AWS reports similar results: semantic caching reduced latency from 3.2 seconds to under half a second. That’s not a minor tweak. That’s turning a frustrating experience into a seamless one. Caching in AI apps isn’t just about speed. It’s about survival. If your budget can’t handle $0.0012 per query (the cost of a non-cached RAG call), you’re not building an AI product-you’re running a money pit.What You Can Actually Cache
Not every AI response is cacheable. You can’t cache a personalized medical diagnosis or real-time stock advice. But here’s what you can:- Common customer service questions ("How do I return an item?")
- Standard product descriptions or FAQs
- Repeated internal knowledge queries ("What’s our PTO policy?")
- Static content generated from templates (email drafts, report summaries)
Four Types of Caching (and Which One to Use)
There are four main ways to cache in AI apps. Each has trade-offs.1. Exact-Match Prompt Caching
This is the simplest: store the exact user input and its output. If someone types "Explain quantum computing in simple terms," you save that exact string and the response. Next time they (or someone else) types the same thing, you serve it instantly. Pros: Easy to implement with Redis. Works with any model. Cons: Fails if the user rephrases. MIT research shows 35-40% of similar queries get missed because they’re worded differently.2. Semantic Caching with Vector Search
This is the game-changer. Instead of matching text, you convert the prompt into a numerical vector-a mathematical representation of its meaning. Then you compare it to stored vectors to find the closest match. AWS’s MemoryDB with vector search does this. If someone asks "How do I fix a leaky faucet?" and you’ve cached "What should I do if my sink is dripping?", it still finds the right answer. Pros: Handles paraphrasing. Reduces latency to under 0.5 seconds. AWS saw 65% cost reduction. Cons: Adds 150ms of overhead to compute the vector. Requires more memory. Harder to debug.3. Object Caching
This caches the results of database queries or API calls that feed into your AI system. For example, if your AI pulls product inventory data from a SQL database, cache that data instead of hitting the DB every time. Pros: Reduces load on backend systems. Works well with Redis or Memcached. Cons: Doesn’t help with the AI model’s own inference cost. Only speeds up data retrieval.4. Page Caching
If your AI generates static HTML pages (like a help center article), cache the entire page using a CDN or reverse proxy like Varnish. Pros: Blazing fast. Near-zero server load. Cons: Only works for non-dynamic content. Useless for real-time chat.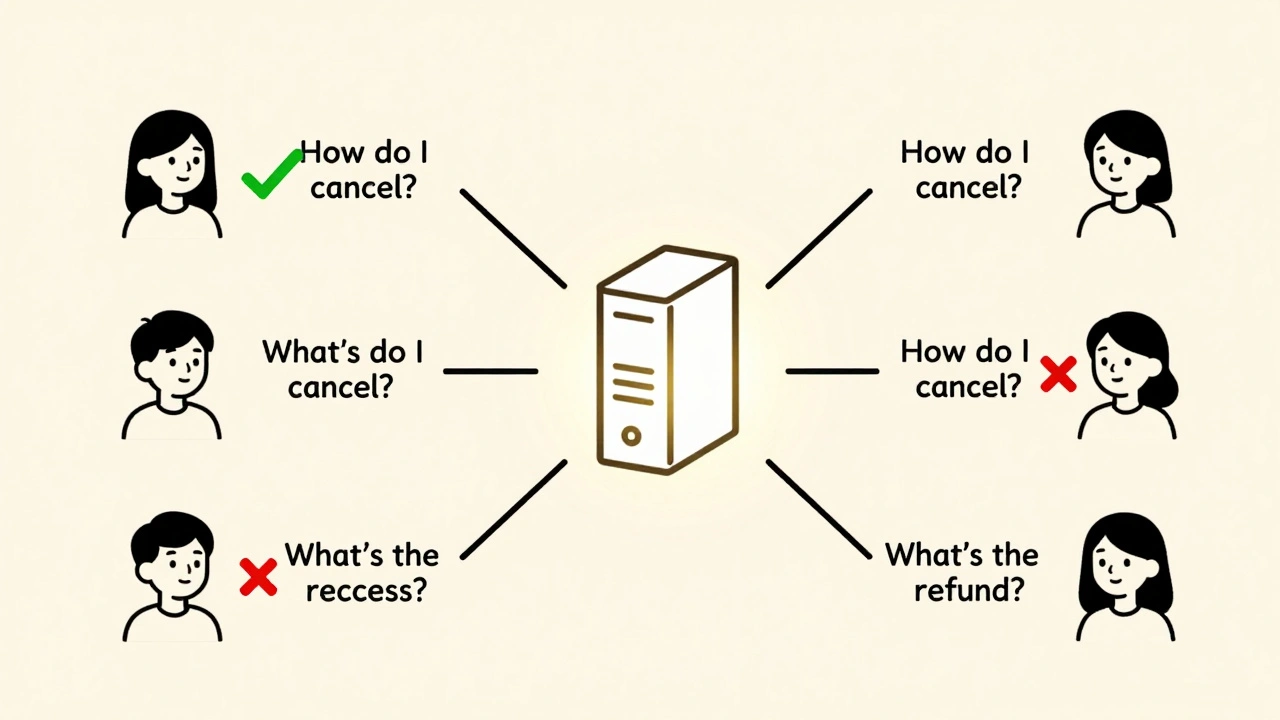
Where to Start: A Practical 4-Step Plan
You don’t need to build a perfect system on day one. Start here:- Identify your top 5 most frequent prompts. Use your app’s analytics. Look for repeats. If a question appears more than 20 times a day, it’s worth caching.
- Choose your tool. For most teams: Redis. It’s reliable, well-documented, and handles strings, JSON, and TTLs easily. If you’re already on AWS and need semantic matching, go with MemoryDB.
- Implement a basic cache layer. Before calling your AI model, check if the exact prompt exists in Redis. If yes, return it. If not, run the model, save the result, then return it. Add a TTL of 24 hours for static content.
- Measure the impact. Track latency before and after. Check your cloud bill. You’ll likely see a 50%+ drop in API costs within the first week.
Pitfalls That Break Caching (And How to Avoid Them)
Caching sounds simple. Until it isn’t.Pitfall 1: Stale Data
You cache a product price of $29.99. The price drops to $19.99. Users still see the old number. That’s bad. Solution: Use short TTLs for dynamic data. For prices or inventory, set TTL to 5-15 minutes. For FAQs, 24 hours is fine. Some teams use hybrid systems: cache with TTL, but trigger a cache refresh when the underlying data changes (like a product update in your CMS).Pitfall 2: Cache Misses for Paraphrased Queries
"How do I cancel?" vs. "What’s the cancellation process?"-same intent, different words. Exact-match caching fails here. Solution: Move to semantic caching. It’s more complex, but worth it. Libraries like Sentence-BERT or OpenAI’s embeddings API can convert text to vectors. Even a basic vector cache cuts miss rates by 60%.Pitfall 3: Cache Pollution
Someone spams your app with nonsense prompts. Now your cache is full of garbage. Solution: Set a max cache size. Use Redis’s LRU (Least Recently Used) eviction policy. It automatically removes old or unused entries.Pitfall 4: No Monitoring
If you don’t track cache hit rates, you don’t know if it’s working. Solution: Log every cache hit and miss. Aim for a 60%+ hit rate. Below 40%? You’re caching the wrong things. Revisit your top prompts.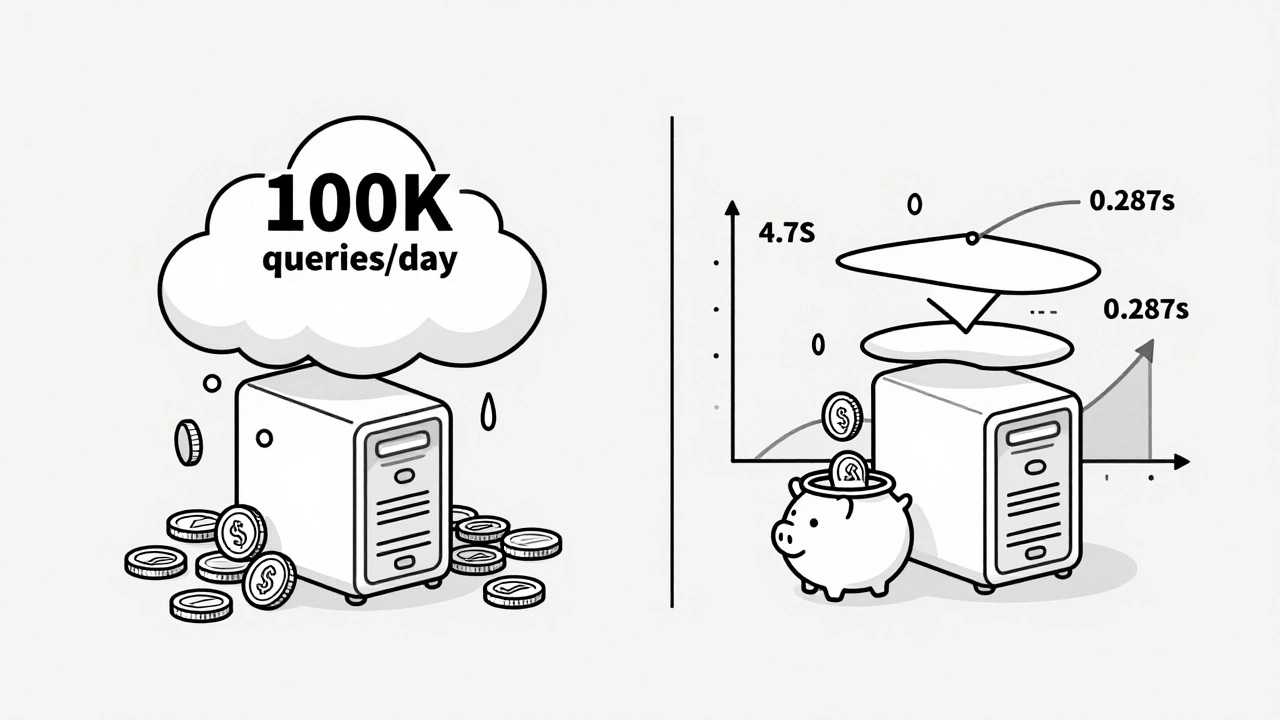
Tools of the Trade (2025 Edition)
You don’t need to build everything from scratch.- Redis: Best for general use. Handles strings, JSON, lists. Supports persistence (RDB/AOF). Used by 42% of AI teams. 4.5/5 stars on G2.
- AWS MemoryDB: Best for semantic caching. Native vector search. Tight integration with Bedrock and SageMaker. 68% of AWS users say it "seamlessly integrates."
- Valkey: Open-source fork of Redis. Growing fast. Good if you want to avoid vendor lock-in.
- Memcached: Simple, fast, but no persistence. Good for temporary caching.
What’s Next? The Future of AI Caching
The next wave isn’t just caching-it’s smart caching. Amazon’s new "Adaptive Cache" uses machine learning to predict which entries to keep or evict. Early tests show 18% higher hit rates. InnovationM is testing "federated caching"-sharing cached responses across data centers to reduce cross-region latency. Gartner predicts that by 2026, 85% of enterprise AI apps will use multi-layer caching: exact-match for simple queries, semantic for paraphrased ones, and object caching for backend data. The bottom line? Caching isn’t a luxury. It’s the backbone of scalable AI. Without it, your app is slow, expensive, and fragile. With it, you unlock speed, savings, and stability.Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need to cache everything in my AI app?
No. Only cache repetitive, low-risk queries-like FAQs, standard responses, or static content. Don’t cache personalized, time-sensitive, or highly variable inputs like medical advice or real-time stock updates. Focus on the 60-70% of queries that repeat. That’s where you get the biggest return.
Can I use Redis with OpenAI or Anthropic models?
Yes. Redis works with any AI model that accepts text prompts. You just need to intercept the API call: check Redis for the prompt first, and if it’s not there, send it to OpenAI or Anthropic, then store the response. Many developers use libraries like redis-py or Node.js Redis clients to handle this automatically.
How do I know if my cache is working?
Track your cache hit rate. If 60% or more of requests are served from cache, you’re doing well. If it’s below 40%, you’re caching the wrong prompts. Use Redis’s INFO command or your cloud provider’s metrics dashboard to monitor hits vs. misses. Also check your API costs-after caching, they should drop by at least 50%.
Is semantic caching worth the extra complexity?
If your users phrase questions differently, yes. Exact-match caching misses up to 40% of similar queries. Semantic caching reduces that to under 10%. The trade-off is a small latency hit (150ms) to generate vector embeddings. But for customer service bots or knowledge bases, the improved accuracy and lower cost make it worth it.
What happens if my cache server goes down?
Your app should still work. Always design for fallback: if Redis or MemoryDB is unreachable, skip the cache and call the AI model directly. Log the event, but don’t let a cache outage break your service. Use short TTLs and monitor cache health so you can recover quickly.

 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence


Sandeepan Gupta
December 14, 2025 AT 07:49Exactly. I saw a startup burn $8k/month on OpenAI just answering "Where’s my order?" 10k times a day. We implemented Redis exact-match caching in 3 days. Costs dropped to $2.4k. Latency went from 3.8s to 190ms. No magic, just math.
Track your top 10 prompts. If it’s repeated more than 15 times/day, cache it. Simple.
Tarun nahata
December 15, 2025 AT 17:44Bro. This isn’t just smart-it’s a game-changer. 🚀 We were drowning in API bills until we flipped the switch on semantic caching. Now our chatbot feels like it reads minds. Users think we’re wizards. We just saved $12k/month and made customers smile.
Stop treating AI like a magic box. Treat it like a lazy intern who needs a cheat sheet. They’ll thank you later.
Aryan Jain
December 16, 2025 AT 14:23They don’t want you to know this. Caching? It’s not about efficiency. It’s about control. Big Tech wants you to keep paying for every single query so they can track your users, sell your data, and lock you into their ecosystem.
Redis? It’s a Trojan horse. They’ll make you dependent. Then they’ll raise prices. You think you’re saving money? You’re just trading one bill for a slower, sneakier one.
What if your cache gets hacked? What if your vector embeddings get poisoned? No one talks about this. But it’s happening. You’re being manipulated into building a fragile house on sand.
Nalini Venugopal
December 18, 2025 AT 07:19Love this breakdown! I’m a dev lead at a SaaS startup and we implemented semantic caching last month using Sentence-BERT + Redis. Our hit rate jumped from 32% to 68% in two weeks. Users are no longer rage-quitting after 3 seconds.
Pro tip: Use TTLs based on data sensitivity. FAQ? 24h. Price? 15m. And always log cache misses-you’ll be shocked what people are actually asking.
Pramod Usdadiya
December 20, 2025 AT 03:41i think u r right about caching but i think u shud also think about the user experiance. like if u cache to much then the user might feel like the bot is not real or its not learning. i mean we want ai to feel alive right? not like a robot repeating the same thing over and over.
also i used redis but had issue with memory on my vps. maybe try memcached for smaller apps?
Aditya Singh Bisht
December 21, 2025 AT 02:10Let me tell you something-this isn’t just about saving money. It’s about respect. Every time you make a user wait 4 seconds for a simple answer, you’re saying their time doesn’t matter.
We went from 4.7s to 287ms. Our NPS went from -12 to +41. People started leaving reviews saying "this feels like magic"-but it wasn’t magic. It was a 10-line Redis check.
You don’t need a PhD to fix this. You just need to stop being lazy. Start with your top 5 prompts. Do it today. Your future self will high-five you.
Agni Saucedo Medel
December 22, 2025 AT 17:56YES! 🙌 I just implemented semantic caching with AWS MemoryDB and now my support bot feels like a real person 😍 Users keep saying "you get me!"-even though I’m just matching vectors. And my cloud bill? Down 72%! 🎉
Also, if you’re using OpenAI, just use their built-in caching tools. No need to reinvent the wheel. Start small, celebrate wins, and don’t overthink it 💖